Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Beijing Institute for Advanced Study, National University of Defense Technology, Beijing 100020, China
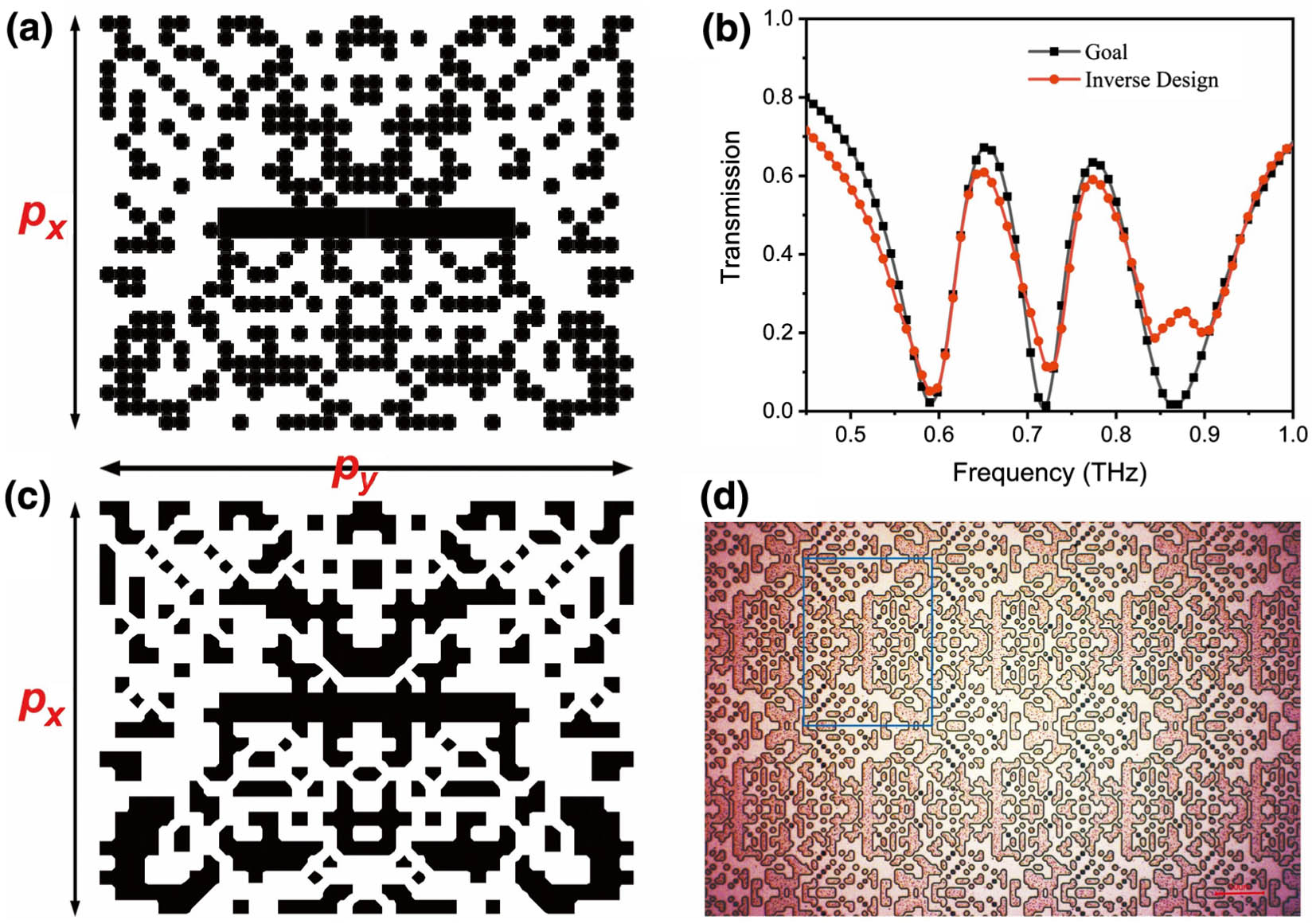
Terahertz metasurfaces have great applications for efficient terahertz modulation, but there are still problems in designing terahertz metadevices in terms of complexity and inefficiency. Herein, we demonstrate an inversely-designed terahertz metasurface with double electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT)-like windows by incorporating a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm with the finite-difference time-domain method. We prepared and tested the metadevices, and the experimental terahertz signals are close to the designed results. By hybridizing amorphous germanium film with the inversely-designed metasurface, two EIT-like windows, including transmission and slow-light effect, exhibit ultrafast modulation behavior in 25 ps excited by a femtosecond laser. The modulation depths of transmission in two transparency windows are 74% and 65%, respectively. The numerical simulations also illustrate the ultrafast dynamic process and modulation mechanism, which match well with the experiment results. Our work thus offers opportunities for designing other objective functions of the terahertz metadevice.
terahertz metasurfaces inverse design double electromagnetically induced transparency Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(11): 113701

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Beijing Institute for Advanced Study, National University of Defense Technology, Beijing 100020, China
Metasurface plays a key role in various terahertz metadevices, while the designed terahertz metasurface still lacks flexibility and variety. On the other hand, inverse design has drawn plenty of attention due to its flexibility and robustness in the application of photonics. This provides an excellent opportunity for metasurface design as well as the development of multifunctional, high-performance terahertz devices. In this work, we demonstrate that, for the first time, a terahertz metasurface supported by the electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) effect can be constructed by inverse design, which combines the particle swarm optimization algorithm with the finite-difference time-domain method. Incorporating germanium (Ge) film with inverse-designed metasurface, an ultrafast EIT modulation on the picosecond scale has been experimentally verified. The experimental results suggest a feasibility to build the terahertz EIT effect in the metasurface through an optimization algorithm of inverse design. Furthermore, this method can be further utilized to design multifunctional and high-performance terahertz devices, which is hard to accomplish in a traditional metamaterial structure. In a word, our method not only provides a novel way to design an ultrafast all-optical terahertz modulator based on artificial metamaterials but also shows the potential applications of inverse design on the terahertz devices.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(6): 06001099

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 National Innovation Institute of Defense Technology, Academy of Military Sciences PLA China, Beijing 100010, China
3 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Computing, College of Computer, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
4 Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences, Beijing 100193, China
5 Science and Technology on Surface Physics and Chemistry Laboratory, Jiangyou 621908, China
Helicity-dependent ultrafast spin current generated by circularly polarized photons in topological materials holds the crux to many technological improvements, such as quantum communications, on-chip communication processing and storage. Here, we present the manipulation of helicity-dependent terahertz emission generated in a nodal line semimetal candidate Mg3Bi2 by using photon polarization states. The terahertz emission is mainly ascribed to the helicity-dependent photocurrent that is originated from circular photogalvanic effects, and the helicity-independent photocurrent that is attributed to linear photogalvanic effect. Our work will inspire more explorations into novel nodal line semimetals and open up new opportunities for developing ultrafast optoelectronics in the topological system.
terahertz spin photocurrent nodal-line semimetal topological material Opto-Electronic Advances
2020, 3(12): 12200023

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Computer, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 National Innovation Institute of Defense Technology, Beijing 100010, China
We experimentally demonstrate for the first time an active all-optical ultrafast modulation of electromagnetically induced transparency-like effect in a hybrid device of sapphire/Si/metamaterial. From numerical simulations, it can be deducted that the tuning process is attributed to the coupling between the dark mode existing in split-ring resonators and the bright mode existing in cut wire resonators. The transmission amplitude modulation is accompanied by the slow-light effect. In addition, the ultrafast formation process is measured to be as fast as 2 ps. This work should make an important contribution to novel chip-scale photonic devices and terahertz communications.
terahertz metamaterials ultrafast photoswitching electromagnetically induced transparency all-optical device Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(9): 092402

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Computer, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 National Innovation Institute of Defense Technology, Academy of Military Sciences PLA China, Beijing 100071, China
Metamaterials play an important role in the modulation of amplitude and group delay in the terahertz (THz) regime on account of their optical properties, which are rare in natural materials. Here an ultrafast anisotropic switch of the plasmon-induced transparency (PIT) effect is experimentally and numerically demonstrated by metamaterial devices composed of two pairs of planar split-ring resonators and a pair of closed-ring resonators. By integration with a germanium (Ge) film, a recovery time of 3 ps and a decay constant of 785 fs are realized in the metadevice. Stimulated by the exterior optical pump, the PIT windows at different frequencies are switched off with an excellent property of slow light for vertical and horizontal THz polarizations, realizing an astonishing modulation depth as high as 99.06%. This work provides a new platform for ultrafast anisotropic metadevices tunable for amplitude and group delay.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(3): 03000263
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Performance Computing, College of Computer, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
3 National Innovation Institute of Defense Technology, Academy of Military Sciences PLA China, Beijing 100071, China
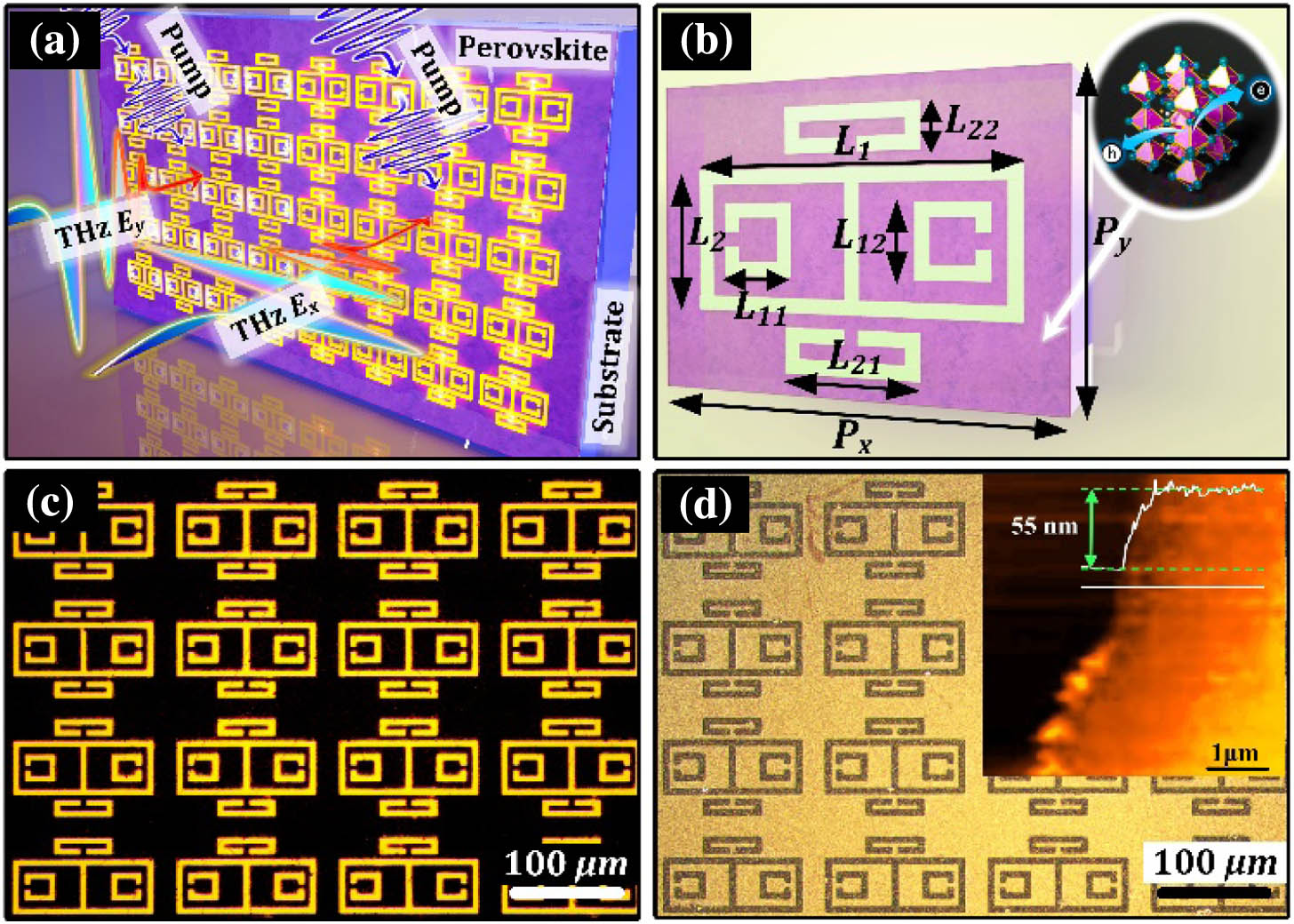
Active control of metamaterial properties with high tunability of both resonant intensity and frequency is essential for advanced terahertz (THz) applications, ranging from spectroscopy and sensing to communications. Among varied metamaterials, plasmon-induced transparency (PIT) has enabled active control with giant sensitivity by embedding semiconducting materials. However, there is still a stringent challenge to achieve dynamic responses in both intensity and frequency modulation. Here, an anisotropic THz active metamaterial device with an ultrasensitive modulation feature is proposed and experimentally studied. A radiative-radiative-coupled PIT system is established, with a frequency shift of 0.26 THz in its sharp transparent windows by polarization rotation. Enabled by high charge-carrier mobility and longer diffusion lengths, we utilize a straightforwardly spin-coated film acting as a photoactive medium to endow the device with high sensitivity and ultrafast speed. When the device is pumped by an ultralow laser fluence, the PIT transmission windows at 0.86 and 1.12 THz demonstrate a significant reduction for two polarizations, respectively, with a full recovery time of 561 ps. In addition, we numerically prove the validity that the investigated resonator structure is sensitive to the optically induced conductivity. The hybrid system not only achieves resonant intensity and frequency modulations simultaneously, but also preserves the all-optical-induced switching merits with high sensitivity and speed, which enriches multifunctional subwavelength metamaterial devices at THz frequencies.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(9): 09000994
国防科技大学 电子对抗学院, 安徽 合肥 230037
通过引入双温方程电子数密度模型, 德鲁德模型和波纹间隔理论?撰=?姿/2S, 得到高频波纹周期具有波长依赖性的特点, 分析了在辐射光通量接近损伤阈值时, 高频周期波纹在一定范围内接近λ/6~λ/4, 且随入射激光通量近似成正比。同时基于时域有限差分法(FDTD)的方法对飞秒激光辐照硅表面电场分布进行数值仿真, 在初始脉冲形成近波长波纹的情况下, 硅表面的电场再分布使得激光能量大多沉积在凹槽边缘, 产生高频周期性结构。在此基础上对初始凹槽深度和激发态下硅表面的光学性质(介电常数)进行分析, 得到了形成高频周期波纹的条件。该研究对于理解飞秒激光造成硅表面形成周期结构及其在加工硅材料领域具有重要的参考意义。
双温方程 高频周期性结构 德鲁德模型 二次谐波 two-temperature equation HSFL Drude model second-harmonic 红外与激光工程
2018, 47(1): 0106003
脉冲功率激光技术国家重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230037
自从第一次观察到飞秒激光大气成丝后, 光丝备受科学家的关注。它的潜在应用价值主要包括电子加速、激光雷达远程遥感、太赫兹辐射和超短脉冲压缩。利用数值仿真的方法, 通过改变艾里光束的衰减系数, 研究了不同能量背景的环形艾里光束飞秒激光大气成丝特性, 得到的光丝长度长于拥有相同峰值功率、弱能量背景高斯光束形成的光丝。通过分析飞秒激光光丝演化过程的时间和空间特性, 发现了环形能量背景是环形艾里光束沿传播方向形成高能量密度光丝的前提条件。比较了环形艾里光束和高丝光束在成丝过程中的光谱展宽特性, 发现不同衰减系数的环形艾里光束具有相似的光谱展宽特性, 但要明显弱于高斯光束的光谱展宽。研究成果对与提升飞秒激光成丝效果具有参考意义。
飞秒激光 艾里光束 克尔效应 自聚焦 femtosecond laser Airy beam Kerr-effect self-focusing 红外与激光工程
2017, 46(8): 0806005
脉冲功率激光技术国家重点实验室(电子工程学院), 安徽 合肥 230037
基于0.53 μm、1.06 μm激光双波长复合输出技术在**上的应用前景, 针对光电对抗双波长复合输出激光器的热效应, 利用泊松热传导理论, 考虑晶体与外界的热交换, 建立了更精确的边界条件, 仿真分析了三向泵浦、内腔倍频情况下激光晶体热透镜效应和倍频晶体热致相位失配的形成过程, 分析讨论了平凸腔补偿热透镜效应的有效性和一般规律。通过实验探究了热效应对双波长复合激光光束质量的影响, 验证了平凸腔对热效应的补偿效果, 发现平凸腔能增大基模模体积, 抑制高阶模增益, 改善复合激光光束质量, 热效应补偿效果会随着补偿平凸镜曲率半径的减小而增强。
全固态激光 双波长复合输出 热效应补偿 光电对抗 all-solid-state laser dual-wavelength composite output compensation of thermal effect electrooptical countermeasures 红外与激光工程
2017, 46(4): 0406003





